

Construction Marine Profile
Pioneering Excellence in Marine Construction and Coastal transformation
We have maintained strong relationships with government bodies,- Port authorities
- Private dredging companies
- Environmental groups and suppliers
- Marine industries, and Coastal sectors
Dredger Services:
- Dredging and reclamation
- Capital and maintenance dredging
- Dredging ports, Marina, harbours, and waterways
- Land reclamation, beach renourishment
- Beach and shore protection
- Environmental mitigation works
- Rock breakwater and revetment construction
- Gas/Oil dredging trenches, pipelines installation
- Marine civil engineering project
Dredging & Reclamation
-
Dredging:
TYPES OF MATERIAL (CSD can dredge)
The CSD cutters power capable to dredge all kinds of material including Gravil, Cobbles, Coarse, They are able to effectively dredge by cutter head. A sediment testing method for evaluating the undrained shear strength of sediments is the shear vane test. The two main types of investigations are desk studies and field sampling. All dredging projects and sites are unique, and the geotechnical site investigation is tailored to the needs of the specific project. Dredging by hydraulic methods mixes about 20% solids with 80% water, which causes bulking. The type of sediment, dredging method, and particle size distribution affect the bulking factor. Ship channels, harbours, and ports experience deposition of fine-grained sediments (silts, clays, and organic matter), which can result in a fluid mud layer above the actual channel bottom.Particle Size Classification of Soil
Types of materials Sizes, mm ————————————————————————————- Clay Less than 0.002
- Silt Fine 002 ~ 0.006
- Silt Medium 006 ~ 0.02
- Silt Coarse 02 ~ 0.06
- Sand Fine 06 ~ 0.2
- Sand Medium 2 ~ 0.6
- Sand Coarse 6 ~ 2
- Gravel Fine 2 ~ 6
- Gravel Medium 6 ~ 20
- Gravel Coarse 20 ~ 60
- Cobbles 60 ~ 200
- Boulders Over 200
The complete dredging spread consists of the CSD as well as a floating pipeline, a sinker line, a land based pipeline, a small tug boat and/or a multi-cat.
As starting-up after preparation process competitions. The cutter suction dredger will mobilized to the work area using towing tug boat and, once arrived, it is positioned by lowering, a spud pole into the seabed and deploying two side and The CSD has two spud poles located at the stern one working spud partially embedded in the seabed, and one auxiliary spud keeps st.by It also the CSD has two anchors system located at both sides of the vessel. The anchors are brought away sideward from the vessel by either anchor booms, the multi-cat or by the small tugboat. The anchors are linked to the ladder of the vessel by winches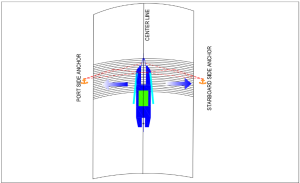
that enable the vessel to move from portside and starboard swinging around the lowered spud pole as shown in the figure below.
To place the anchors by anchors boom, the CSD will rotate to one side and swing out the anchor boom to place the first anchor. The CSD will then rotate to the other side, repeating the process to place the second anchor.
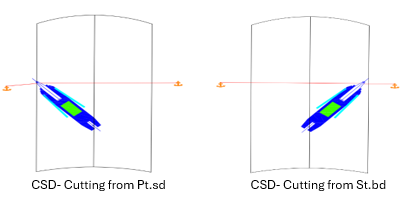
Once the CSD is positioned, the dredging process will begin. The dredger will be pulled by the winches from portside to starboard around the working spud pole, describing arcs of approximately 45 degrees. This way, the cutter head will cut the soil in arcs with a pre-determined width, loosening the material to be dredged.
Once a complete arc is accomplished, the CSD uses a spud carriage to go forward by moving against the working spud, repeating the cutting process in the new position swinging in the opposite direction. Typical progress of a CSD is shown in the figure below.
dredged material is sucked in and mixed with water by the submerged pump and is transported through the on board pipeline up to the inboard pumps. The mixture passes directly through the pumps to be reclamation area of by a closed system of discharge pipelines.
The pipeline discharge system may be composed of a floating pipeline, sinker lines and a shore line that connects the CSD to shore. Thus, the dredged material is directly discharged to the disposal area onshore via closed reclamation bonds walls.
In case the capacity of the pumps on the CSD is not sufficient to pump the material to shore, due to long pumping distances and/or heavy material one or more extra pump(s), booster(s) may be put in between different pipeline sections in order to increase the pump capacity. The system is still a closed system from cutter head to end of the pipeline onshore.
COMMON MARINE EQUIPMENT-CME
Contractor’s or logistics marine vessels are able to start up their engines and are able to move at a short notice period at any time. Should the vessels navigation master controlling the full process of manoeuvring then he will immediately inform the Project Managements, navigation routs and towing operation and wait for instruction to proceed?
Sr. | VESSEL | TYPE | AREA OF WORK |
1) | Dredger CSD | Heavy Duty Cutter Suction Dredger | Dredging and Reclamation. |
2) | Dredger TSHD | Trailing Suction Hopper Dredger | Dredging and transporting sand from borrow area. |
3) | Multi-purpose vessel | Multi-cat | Anchor handling and pipe line works |
4) | Tug Boat | Towing Tug | Dredger towing and shifting |
5) | Crew Boat | 18 to 25+ passenger | Crew Change |
6) | Survey Vessel | Survey Boat | Hydro Survey in the channel,. The survey vessel will be surveyed – In pre-dredge, – Intermediate and – Post dredge surveys |
MULTI-PURPOSE VESSEL
A multi purpose working Vessel (Mutlicat) is a self-propelled vessel, with deck-working space and as minimum equipped with a crane and wire rope-winch . As the name reveals the vessel is used for many operations on site.
Multiact examples of tasks generally executed by this type of vessel are:
- Shifting, installation and dismantling of operation pipelines, pontoons, floaters marine buoys…etc.
- Handling of floating lines submersible line job.
- Pipeline anchor handling job.
- Supplying the dredger with spare parts and consumables
- Assistance shore connections installation

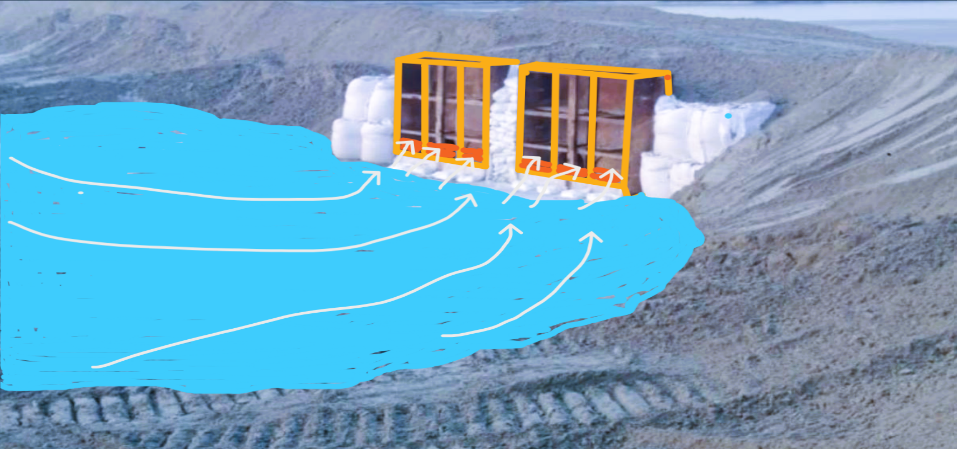
De-Watering Boxes
2. Reclamation Work Description
The reclamation area will be prepared to receive the dredged material prior to start of the dredging works. The main scope prior to the starting of the reclamation by dredger is containment in a form of bunds which will be constructed through pumping then water boxes to be installed to monitor the water de-watering system (See figure)
In case of installation of a silt screen, the silt screen condition and arrangement shall be monitored throughout the construction period including water quality monitoring as per EAD guidelines and in accordance with Environmental MP.
Bunds will be created by dozers using original onshore material and reinforced by dredged material, through fast progression on the reclamation. The shore pipe will be placed at a pre-determined offset and material discharged will be pushed by dozers and excavators to create the containment bund.
Reclamation bund construction
At the reclamation area, land based equipment such as excavators, bulldozers and wheel loaders, also associated staff, operators and labours will handle the pipelines and spreading of the dredging material over the allocated area on layers as required by clients.
COMMON LAND EQUIPMENT – CLE
| Sr. | MACHINE | TYPE | AREA OF WORK |
1 |
Excavator
|
CAT 330 or similar |
Loading material, pipe handling |
2 |
Wheel Loaders |
Cat 966 or similar with pipe bucket |
Loading material, pipe handling |
3 |
Trucks |
20m³ – 45m³ |
Transport of Material (If required) |
4 |
Bull Dozers |
CAT D6 – CAT D8 or similar |
Pushing material |
5 |
Water Tanks |
2000gal – 4500 gal |
Dust control for temp. roads |
6 |
Diesel Trucks |
1000gal – 5000gal |
Fuel distribution |
Pipelines
A network of steel pipes will be used as discharge pipeline from the dredging equipment to the disposal area, which consist of on board, floating and land based pipelines. The on board pipeline is part of the equipment and carries the mixture from the main pump to the stern end of the dredger.
Reclamation Site
Pipes with flexible joints, floating by means of floating steel pontoons, are connected to the on-board pipelines. This flexible floating pipeline transports the discharge material over water from the dredger to the shore, optionally via a sinker line, where it is connected to the shore pipeline. The shore pipes are laid out on land and are joined using bolt/nut connections or push pipe/fast connections will be used.

Reclamation Site
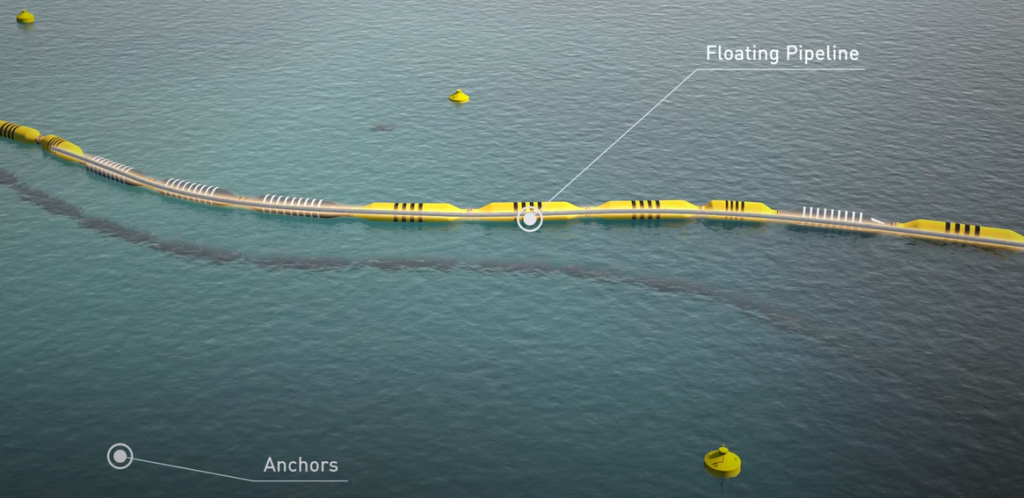
Floating pipelines